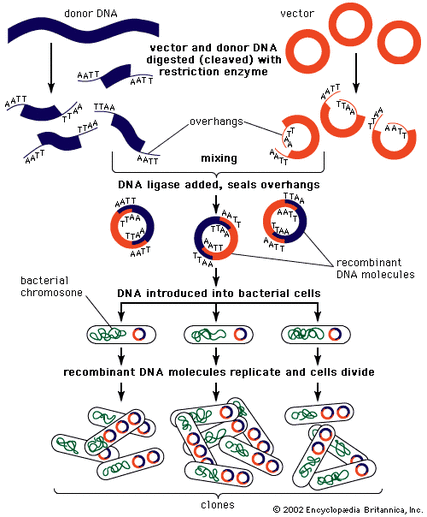
The Discovery of Recombinant DNA (rDNA)
The discovery of gene therapy would not have been proficiently achievable without the discovery of recombinant DNA (rDNA). Recombinant DNA is carried out through the use of enzymes, which recognize specific sequences, and are signaled to "cut" the DNA strands at those specific locations. This significant method has led scientist to be able to recognize the location of genes, regardless of their known function.
In 1972, scientists created the first recombinant DNA molecule by inserting DNA strands of one species into that of a different species. The following year, scientists were able to raise a colony of the rDNA molecules through multiplications of the single molecule. Thereafter, scientific and political meetings were held with the aim of formulating guidelines for research, as well as addressing the ethical concerns dealing with safety issues in the laboratory. With the establishment of "splitting" genes, scientists were able to develop two additional techniques to determine the DNA sequences which contain all genetic information. Thus they were able to analyze and inspect individual genetic material and their carried out functions generated by the DNA sequence. —
In 1972, scientists created the first recombinant DNA molecule by inserting DNA strands of one species into that of a different species. The following year, scientists were able to raise a colony of the rDNA molecules through multiplications of the single molecule. Thereafter, scientific and political meetings were held with the aim of formulating guidelines for research, as well as addressing the ethical concerns dealing with safety issues in the laboratory. With the establishment of "splitting" genes, scientists were able to develop two additional techniques to determine the DNA sequences which contain all genetic information. Thus they were able to analyze and inspect individual genetic material and their carried out functions generated by the DNA sequence. —
Bacterial Plasmids
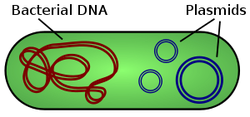
—To manipulate genes in the laboratory, biologists often use bacterial plasmids, which are small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the larger bacterial chromosome.
—These plasmids are capable of carrying virtually any gene, and pass that gene from one generation to the next, they are key tools for gene cloning, the production of multiple identical copies of a gene carrying piece of DNA.
—These plasmids are capable of carrying virtually any gene, and pass that gene from one generation to the next, they are key tools for gene cloning, the production of multiple identical copies of a gene carrying piece of DNA.
Recombinant DNA Process
—This genetic engineering can serve a variety of purposes, from basic research to medical applications.
(i.e. Vaccines, Gene Therapy)
(i.e. Vaccines, Gene Therapy)
A New Biotechnology Firm, 1976
Following the establishment of the first new firm of biotechnology in 1976, more than 100 other firms have been founded for the purpose of advancement in applying recombinant DNA technology to medicine and other areas. In addition, the commercial market had grown more interest when the first commerical product was developed from rDNA in 1982, human insulin, or Humulin.
History of Genetic Diseases
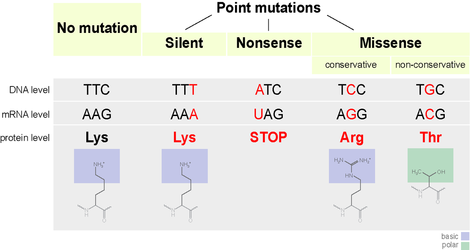
Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA is called a mutation. Mutations within a gene can be divided into two general categories:
nuecleotide substitution and nucleotide insertions or deletions.
Each nucleotide codes for a specific amino acid which is the building block of proteins. A change in one base of a nucleotide can result in a misread--and inefficiency of a protein.
After scientists realized the power of DNA technology, they, as well as society quickly became concerned about its potential dangers. Subsequently, scientists developed a set of guidelines that have now become formal government regulations in the United States and other parts of the world.
One safety measure is a set of strict laboratory procedures to protect researchers from infection by engineered microbes and to prevent microbes from accidentally leaving the laboratory. In addition, strains of microbes to be used in recombinant DNA experiments are genetically crippled to ensure that they cannot survive outside the laboratory. Finally, certain obviously dangerous experiments have been banned.
nuecleotide substitution and nucleotide insertions or deletions.
Each nucleotide codes for a specific amino acid which is the building block of proteins. A change in one base of a nucleotide can result in a misread--and inefficiency of a protein.
After scientists realized the power of DNA technology, they, as well as society quickly became concerned about its potential dangers. Subsequently, scientists developed a set of guidelines that have now become formal government regulations in the United States and other parts of the world.
One safety measure is a set of strict laboratory procedures to protect researchers from infection by engineered microbes and to prevent microbes from accidentally leaving the laboratory. In addition, strains of microbes to be used in recombinant DNA experiments are genetically crippled to ensure that they cannot survive outside the laboratory. Finally, certain obviously dangerous experiments have been banned.